Electromagnetic interference (EMI) is a critical issue in any electronic design. This interference, which originates from both natural and artificial electromagnetic sources, can introduce unwanted noise into electrical circuits, potentially degrading or even crippling system performance. The challenge of managing EMI becomes increasingly complex and significant as technology advances, particularly with the advent of faster applications like 5G mm Wave.
However, engineers and designers can take proactive steps to protect their systems from EMI-related damage. The key is to address EMI during the initial design phase. By acknowledging the risk of EMI early on and creating products resilient to its effects, many future problems, unexpected expenses, and delays can be avoided. Engineers should focus on four essential aspects when designing with EMI in mind: electrical, physical and mechanical, environmental, and commercial factors. A comprehensive understanding of these design requirements allows for the integration of suitable solutions to counteract EMI.
After incorporating EMI mitigation strategies into the design, the next step is to select appropriate EMI shielding products. Options abound, with some of the most commonly used including EMI shielding gaskets, shielding paints, and thermal gap fillers.
EMI Shielding Gaskets
EMI shielding gaskets are crafted to block electromagnetic waves from penetrating or escaping an electronic enclosure. These gaskets are available in a wide range of materials and configurations to suit diverse applications across various industries. Options include electrically conductive elastomers, robotically dispensed form-in-place materials, fabric-over-foam solutions, and traditional metal-based gaskets.
EMI Shielding Paints
Electrically conductive paints and coatings offer a protective barrier for various applications that are highly susceptible to EMI. This type of shielding material is particularly beneficial for plastic and composite housings in electronic assemblies, as well as aircraft and airframe components.
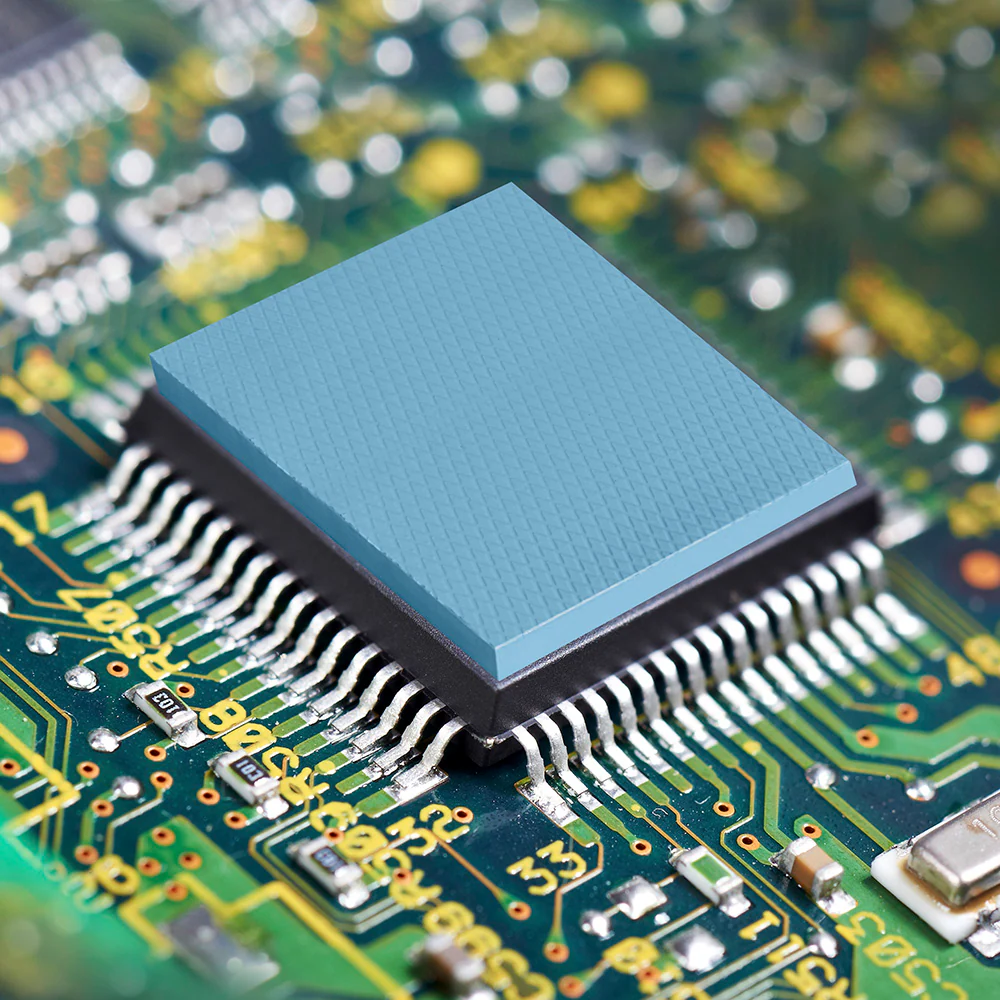
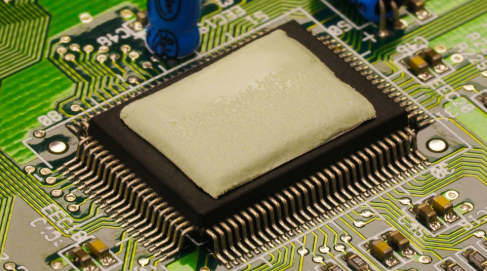
Thermal Gap Fillers
A crucial factor in minimizing EMI is addressing the gaps between heat-generating and heat-dissipating surfaces. Thermal gap fillers, available in pad and gel forms, are specifically engineered to bridge these gaps, thereby reducing the risk of EMI.
(Request Sample Today)