Product Description
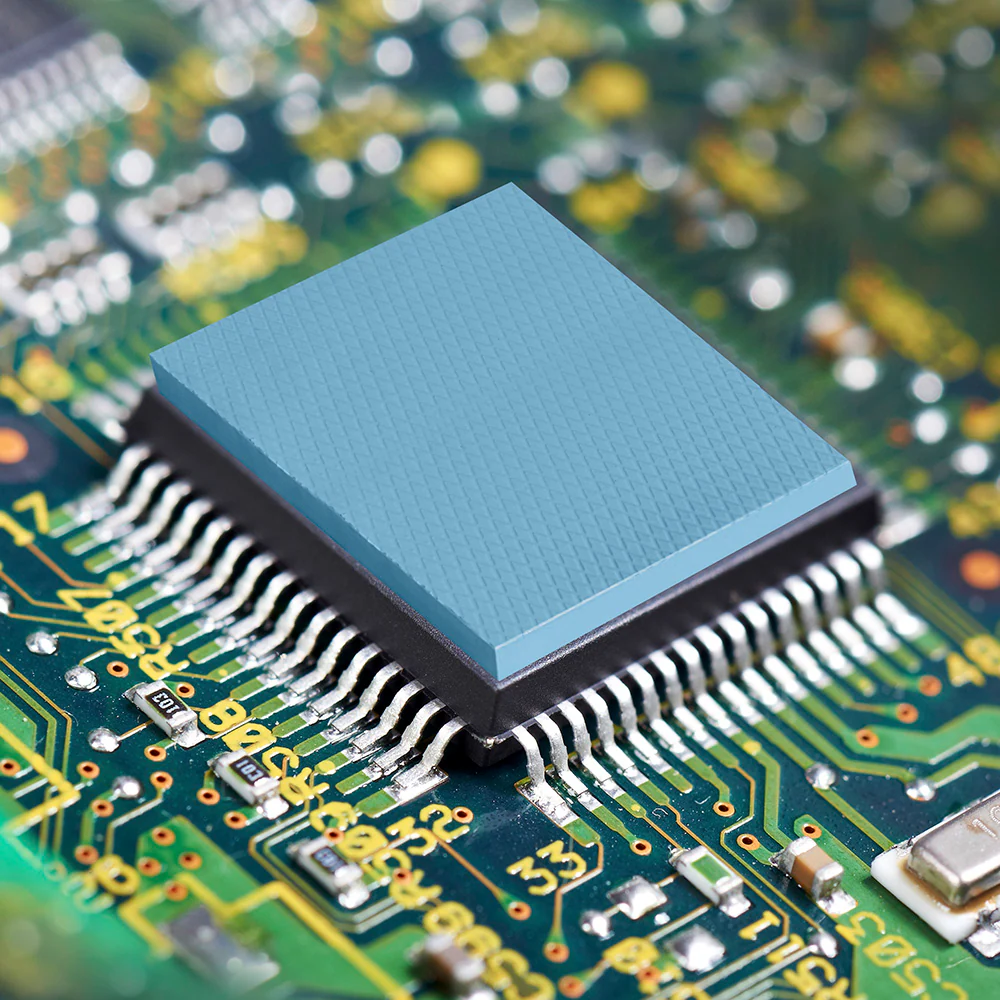
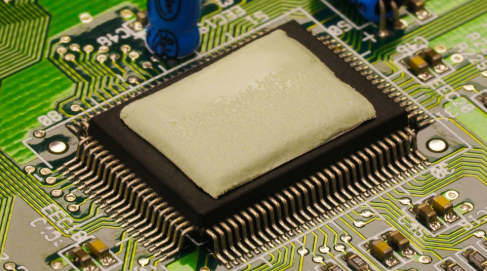
Matrix low closure force gaskets feature specialized foam materials like silicone, urethane, and EPDM. These gaskets provide engineers with the advantage of achieving reliable sealing at minimal compression force. This reduces stress on delicate components, prevents over-compression, and ensures longer-lasting equipment integrity. They are widely used in industries such as electronics, medical devices, and aerospace, where protecting sensitive components while maintaining a secure seal is critical for operational efficiency and product reliability.


Value Added
Matrix enhances its value as a low closure force gasket partner through comprehensive in-house capabilities, including fabrication, vulcanizing, die cutting, Form-in-Place (FIP), and XY cutting. These advanced processes allow engineers to achieve precise customization, optimal material utilization, and efficient integration, ensuring impeccable sealing performance at minimal compression forces, particularly beneficial in delicate component protection and achieving optimal sealing solutions.
Frequently asked questions
If you have a question that is not addressed in our FAQ please click 'Contact Matrix' at the top of the page and submit. We will answer directly and add it to our FAQ to benefit the entire engineering community.
Your vision! Our expertise! Collaborating with engineering teams is what we do best! We listens to your priorities, and create a customized solution tailored to your specific requirements.
1. Silicone Low Compression Force Materials:
- Description: Silicone-based foam materials engineered for minimal compression.
- Primary Benefit: Delicate component protection with reliable sealing, ideal for electronics and medical devices.
2. Urethane Low Compression Force Materials:
- Description: Urethane foam materials designed for low closure force applications.
- Primary Benefit: Exceptional sealing performance while minimizing stress on components, crucial for sensitive electronics.
3. EPDM Low Compression Force Materials:
- Description: EPDM foam materials optimized for minimal compression requirements.
- Primary Benefit: Reduces over-compression risks, ensuring extended equipment longevity, commonly used in aerospace and automotive.
4. Polyethylene Low Compression Force Materials:
- Description: Polyethylene-based foams engineered for low closure force sealing.
- Primary Benefit: Provides consistent sealing performance with minimal force, vital in industrial equipment.
5. Polyurethane Low Compression Force Materials:
- Description: Polyurethane foam materials for low-compression applications.
- Primary Benefit: Maintains sealing integrity while minimizing component stress, widely used in medical and HVAC systems.
6. Neoprene Low Compression Force Materials:
- Description: Neoprene foam materials designed to require low compression force.
- Primary Benefit: Delivers reliable sealing without excessive pressure, crucial in marine and automotive applications.
7. Nitrile Low Compression Force Materials:
- Description: Nitrile rubber-based foam materials engineered for low closure force.
- Primary Benefit: Ensures secure sealing with gentle compression, suitable for sensitive equipment in various industries.
1. Electronics Enclosures:
- Problem: Preventing damage to fragile electronic components while maintaining a secure seal.
- Solution: Low compression force gaskets made of silicone or urethane in sensitive electronic enclosures.
2. Medical Devices:
- Problem: Ensuring sterile and reliable sealing in medical equipment without damaging delicate instruments.
- Solution: Low compression force gaskets, often silicone-based, in medical devices like diagnostic equipment and surgical tools.
3. Aerospace Electronics:
- Problem: Protecting avionics and sensors while avoiding excessive compression.
- Solution: Low compression force gaskets, including EPDM or neoprene, in aerospace electronics.
4. Optical Equipment:
- Problem: Preserving optical clarity and precision alignment in optical systems.
- Solution: Low compression force gaskets in optical lenses and equipment to avoid distortions.
5. Semiconductor Manufacturing:
- Problem: Sealing semiconductor equipment without compromising sensitive chip production.
- Solution: Low compression force gaskets, often made of polyurethane, in semiconductor manufacturing tools.
6. Automotive Sensors:
- Problem: Ensuring reliable sealing around sensors without affecting accuracy.
- Solution: Low compression force gaskets in automotive sensor enclosures for emissions, parking, and more.
7. HVAC Systems:
- Problem: Sealing air ducts and access points without damaging ductwork or HVAC components.
- Solution: Low compression force gaskets in HVAC systems to maintain sealing efficiency.
8. Food Processing Equipment:
- Problem: Preserving product quality and hygiene while sealing equipment.
- Solution: Low compression force gaskets, such as silicone or nitrile, in food processing machinery.
9. Pharmaceutical Packaging:
- Problem: Ensuring contamination-free sealing of pharmaceutical packaging.
- Solution: Low compression force gaskets for pharmaceutical vials and containers.
10. Laboratory Equipment:
- Problem: Maintaining sterile environments and precise sealing in lab apparatus.
- Solution: Low compression force gaskets in laboratory equipment for research and analysis.
COMPARE
Compare Options
Click below to get a customized comparison chart tailored to your application.
1
2
3
| 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| Consideration | Low Compression Force Gaskets | Conventional Rubber Gaskets | Cork-Rubber Gaskets |
| Compression Force | Very Good | Good | Good |
| Sealing Integrity | Very Good | Good | Good |
| Delicate Component Protection | Very Good | Moderate | Moderate |
| Temperature Resistance | Good | Very Good | Good |
| Chemical Resistance | Good | Moderate | Moderate |
| Compression Set Resistance | Very Good | Moderate | Good |
| Electrical Insulation | Good | Good | Good |
| Material Resilience | Very Good | Good | Good |
| Customization Options | Very Good | Good | Good |
| Cost Efficiency | Moderate | Very Good | Moderate |